What Is A Vacuole In An Animal Cell
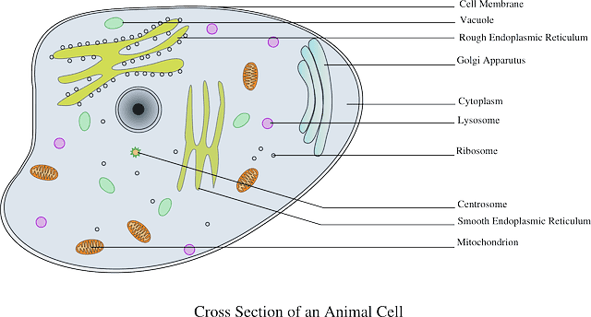
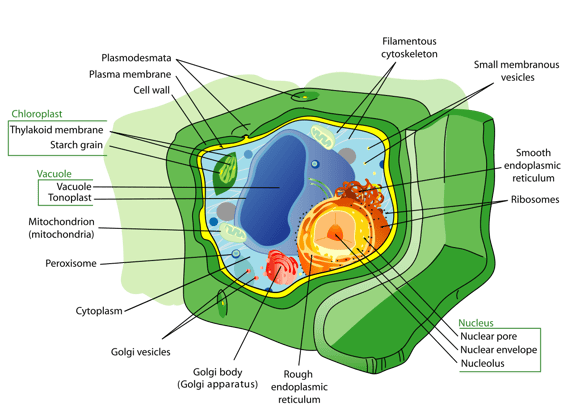
What is a vacuole and what does it do? A vacuole is a structure found in fauna, plant, bacteria, protist, and fungi cells. Information technology's i of the largest organelles found in cells, and information technology's shaped like a large sac. Vacuoles accept a simple structure: they are surrounded by a thin membrane and filled with fluid and any molecules they take in. They look like to vesicles, another organelle, because both are membrane-bound sacs, merely vacuoles are significantly larger than vesicles and are formed when multiple vesicles fuse together. What does the vacuole do? The principal office of vacuoles is to hold various substances and molecules; they basically act like the storage unit of the prison cell. Beneath are some key vacuole functions, many of which chronicle to storing materials that the prison cell will demand later on or which can harm the jail cell and therefore demand to be removed: Remove and store waste produced during autophagy (when role of the jail cell is broken down due to age or impairment) Remove and store harmful strange products so they don't damage the jail cell Store water Store nutrients such as lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates Yet, the precise functions of a vacuole depend on the type of cell it'south in. In the following sections, nosotros go over boosted functions vacuoles can take, based on whether they're located in animal, found/fungi, leaner, or protist cells. Vacuoles in animal cells mostly shop substances; they aren't needed every bit much for breaking downwards substances because lysosomes, another organelle in animal cells, exercise that. Brute cell vacuoles are typically modest, and each prison cell can contain multiple vacuoles. Vacuoles tin store unlike substances depending on the type of cell they are in. For example, in fat cells, vacuoles will frequently store large amounts of lipids. Vacuoles in animal cells also help with the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis is when substances that can't passively move through the prison cell membrane are actively transported into the cell. These substances tin include anything from nutrients to toxins to cell debris. Exocytosis is the opposite; it'due south the process of actively moving molecules out of a cell. During these processes, the vacuole is where the substances are stored or broken downwards before/after they are moved into/out of the cell. Unlike animal cells, plant cells typically comprise merely one vacuole per jail cell (oftentimes referred to as a "fundamental vacuole"), and the vacuole they comprise is much larger than those in animal cells. Plant cell key vacuoles take upward an enormous percent of the cell, sometimes over 90% of cell space, although 30-50% is more common. Surrounding the vacuoles in mature found cells is an boosted thin membrane called a tonoplast. The tonoplast helps the vacuole hold its structure then that the vacuole can retain its shape. Vacuoles in plant and fungi cells perform very similar functions, however; fungi cell vacuoles are typically much smaller than found cell vacuoles, and each fungi prison cell tin can comprise more than one vacuole (similar to animal cells). Vacuoles in found and fungi cells perform more functions than vacuoles in other types of cells; they're a critical office of keeping the establish/fungi alive and good for you. Because fungi and establish cells don't comprise lysosomes, vacuoles in these cells also break downwards more materials than they do in beast cells. In addition to the functions listed in the previous section, vacuoles in plant and fungi cells also: Maintain proper pH: The vacuole keeps the cytoplasm in the cell acidic so that enzymes can break down different molecules. The vacuole lowers pH by moving protons from the prison cell cytosol into the vacuole. Store water: The vacuole can use proton motive force, a chemical gradient used to motion materials in an out of the cell, to store h2o which allows the plant to survive longer in periods of drought. Maintain turgor pressure: Turgor pressure is the pressure level of the master area of the cell against the cell wall. Information technology's ane of the ways plants and copse avoid being limp and grow tall and potent. Think of fresh, crisp salad greens vs. limp ones. The sometime have high turgor pressure level. Tonoplasts in vacuoles command turgor pressure by maintaining a particular balance of ions, which causes the vacuole to swell against the cell wall. Adjust size of the cell: Because vacuoles in plant cells tin can be so large, they are a fundamental part in determining how large or small a certain plant cell is, which can in turn affect the size of dissimilar parts of the plant. In this image, you lot can meet how much larger the vacuole (big bluish structure) is in a plant prison cell compared to an animal cell. Source: Wikipedia commons Non all types of leaner take cells that contain vacuoles, but for those that practice, they are mostly used for storage. Vacuoles are especially big in some species of sulfur leaner; in these bacteria the vacuoles tin take upwardly equally much infinite or more as vacuoles in plant cells do, up to 98% percentage of the cell'south expanse. These vacuoles are often used to store nitrate ions for later use by the cell. Some cyanobacteria besides have vacuoles that are permeable to gases. Gases tin be moved into or out of the vacuole which gives the bacteria a manner to control their buoyancy. Protists contain a specific type of vacuole called a contractile vacuole. Instead of existence used for storage, this vacuole regulates the amount of water in a cell (known as "osmoregulation"). Protists that alive in freshwater can accept besides much water into their cells, causing them to rupture. The contractile vacuole prevents this by contracting and expelling water from the cell. Some protists have one contractile vacuole per cell, others have multiple. In flagellates such as Euglena, the contractile vacuole remains stationary inside the cell, just in Amoeba, it changes position based on the protist'south movements. In Amoeba, contractile vacuoles too collect waste produced by the cell. A vacuole is an organelle that is institute in many types of cells, including animal, plant, fungi, leaner, and protist cells. The main vacuole function is to shop substances, typically either waste or harmful substances, or useful substances the prison cell will need afterwards. Vacuoles are most important in constitute cells, where they accept boosted functions, such equally maintaining the proper pH and turgor pressure the plant needs to thrive. Now you know about vacuoles, merely what about the remainder of the cell? The c ell theory is a key biological concept you lot'll need to know,and y'all can learn all about information technology in our in-depth guide to cell theory. Are there other science topics y'all want to review? Then you lot're in luck! Our guides will teach y'all loads of useful topics, includinghow to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit and what the density of water is. What are the virtually important science classes to have in high school?Check out our guide to learn all the high school classes you should be taking. Need more assistance with this topic? Check out Tutorbase! Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who tin assist you polish an essay for English language or explain how derivatives piece of work for Calculus. Yous can use dozens of filters and search criteria to discover the perfect person for your needs. 
The iv Main Vacuole Functions
Structure and Function of Vacuoles in Fauna Cells
Construction and Function of Vacuoles in Institute and Fungi Cells
Structure and Function of Vacuoles in Leaner Cells
Construction and Office of Vacuoles in Protist Cells
Summary: Vacuole Definition
What's Next?


Near the Writer
Christine graduated from Michigan Land Academy with degrees in Ecology Biology and Geography and received her Chief'south from Duke University. In high schoolhouse she scored in the 99th percentile on the Sat and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Source: https://blog.prepscholar.com/vacuole-function-definition
Posted by: wolfgodis1942.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is A Vacuole In An Animal Cell"
Post a Comment